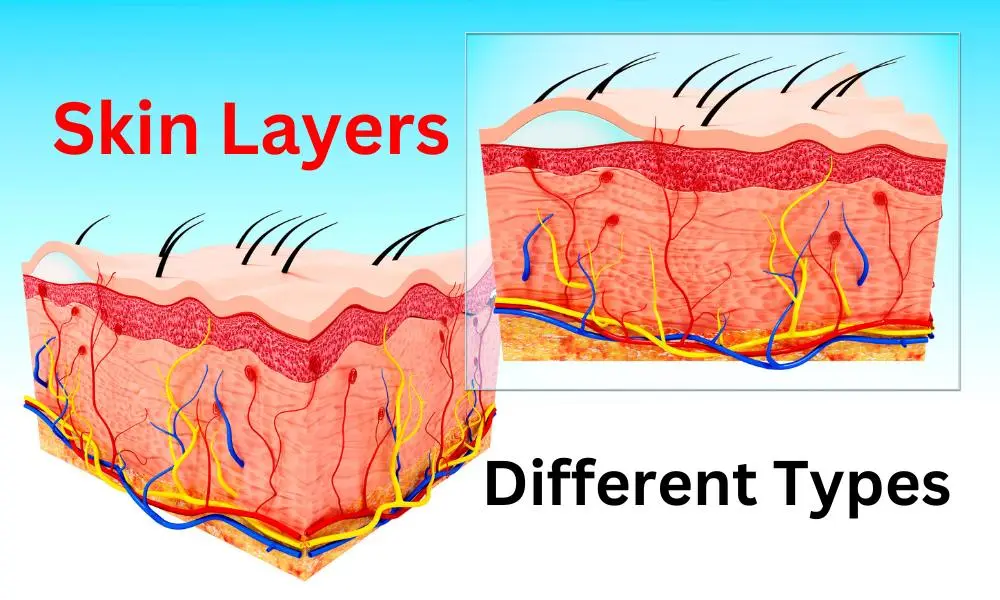
Our skin is not only the largest organ in our body but also one of the most fascinating. Comprising multiple layers, each with its own unique functions, the skin plays a crucial role in protecting our body from external threats while regulating temperature, sensation, and more. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the different types of skin layers, their functions, and key facts about each layer.
Types of Skin Layers:

Mainly 3 layers of skin:
- epidermis
- dermis
- hypodermis
1. The Epidermis: Shielding Your Body
- Outermost Layer: The epidermis forms the skin’s protective outer shell.
- Constant Renewal: It continually renews itself, with old cells shedding and new ones rising to the surface.
- Barrier Function: Acts as a protective barrier against environmental factors such as UV radiation, microbes, chemicals and environmental pollutants.
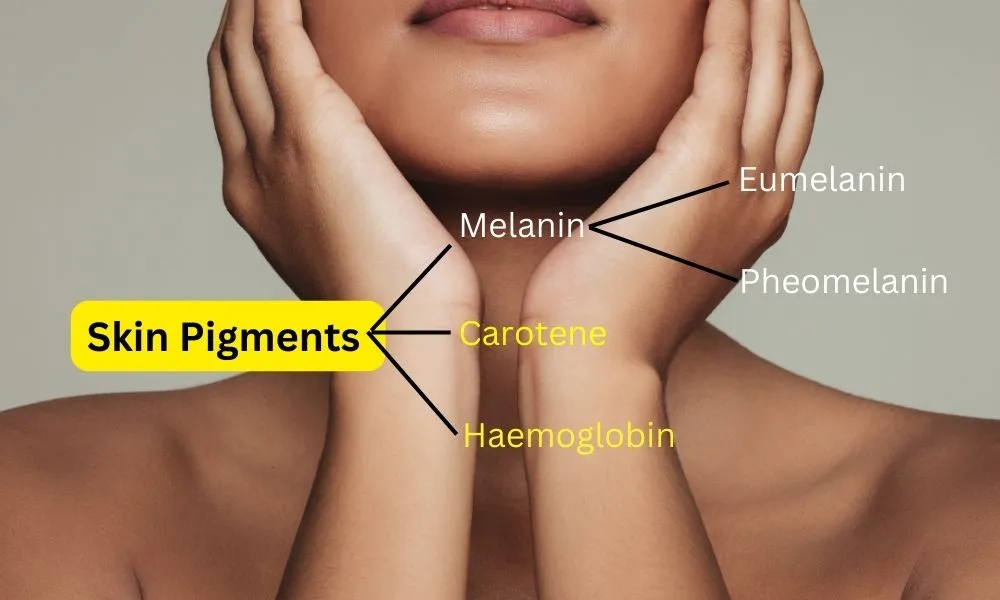
- Melanin Production: The epidermis contains melanocytes, which produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color and protection against UV radiation.
2. The Dermis: The Supportive Layer
- Underlying Layer: Beneath the epidermis lies the dermis, a bustling hub of activity.
- Connective Tissue: Composed of collagen and elastin fibers, providing structure and elasticity.
- Blood Supply: Rich network of blood vessels delivers nutrients and oxygen, regulates temperature, and removes waste.
- Nerve Endings: Houses sensory receptors for touch, pain, and temperature.
- Hair Follicles and Sweat Glands: Embedded within the dermis, contributing to hair growth and sweat production.
3. The Subcutaneous Tissue: Insulation and Cushioning
- Also known as the hypodermis.
- Deepest Layer: The subcutaneous tissue, or hypodermis, resides beneath the dermis.
- Fat Deposits: Comprised of adipose tissue, offering insulation and cushioning.
- Energy Storage: Serves as an energy reservoir, storing excess calories.
- Thermoregulation: Regulates body temperature by conserving or releasing heat.
- Shock Absorption: Absorbs impacts and protects internal organs from injury. (Cushions the body from impacts and pressure.)
- Key Fact: Subcutaneous fat distribution varies among individuals and is influenced by factors such as genetics, age, and hormonal changes.
(Also Read: 4 Hormones That Promote Happiness in Hindi…)
People Also Ask FAQs

Q: How can I keep my skin layers healthy?
Ans: Simple habits like staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, wearing sunscreen, and avoiding harsh chemicals can help keep your skin layers in top shape.
Q: How does aging affect the layers of skin?
Ans: Aging can lead to a decrease in collagen and elastin production, causing the skin to lose its elasticity and firmness. Additionally, the rate of skin cell turnover slows down, resulting in a thinner epidermis and slower wound healing.
Q: Can skincare products penetrate all layers of skin?
Ans: Most skincare products primarily target the epidermis, where they can hydrate the skin, deliver antioxidants, and exfoliate dead skin cells. However, certain ingredients may penetrate deeper into the dermis, depending on their molecular size and formulation.
(Also Read: A Comprehensive Indian Diet Chart for Diabetic Patients…)
Q: What role does diet play in maintaining healthy skin layers?
Ans: A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can support skin health by promoting collagen production, protecting against UV damage, and reducing inflammation. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish and nuts, are particularly beneficial for maintaining skin integrity.
Q: Are there any medical conditions that can affect the layers of skin?
Ans: Yes, various skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, acne, and skin cancer can affect different layers of the skin, leading to symptoms like inflammation, itching, and changes in skin texture.
(Also Read: Different Types of Plants In Hindi…)
Conclusion:
Understanding the different layers of skin is essential for maintaining healthy skin and preventing various skin conditions. By appreciating the roles of the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue, we can make informed decisions about skincare and overall well-being. So, next time you look in the mirror, remember that your skin is not just a surface but a complex and remarkable organ that deserves care and attention.


















Leave a Reply